Transloading is a logistics process that involves transferring cargo or freight from one mode of transportation to another. It is commonly used when goods need to be transported across different regions or countries.
The process involves unloading the cargo from one transportation mode, such as a ship or train, and reloading it onto another mode, such as a truck or plane, for the final leg of the journey.
Transloading offers flexibility, cost savings, and improved efficiency in supply chain operations by optimizing transportation routes and modes. It plays a crucial role in international trade and multimodal transportation.
Read more: How to perfect your Cross-docking process
Table of Contents
What is Transloading?
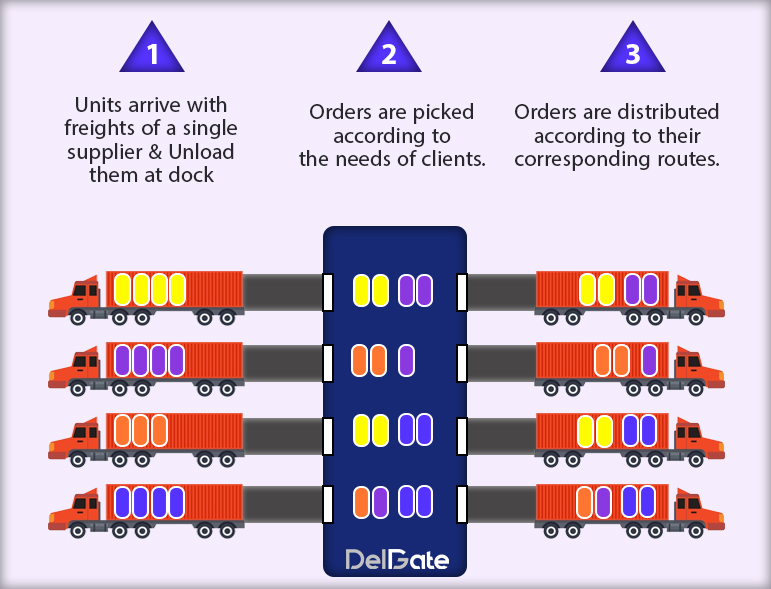
transloading in 3pl logistics is a technique that utilizes in 3pl logistics to optimize the supply chain. In this process, the goods do not store in the warehouse, and it usually occurs at a distribution connection terminal in a warehouse.
In fact, Transloading is a distribution system that unloads goods from inbound delivery conveyances and loads them directly onto outbound conveyances. This technique eliminates storing and collecting orders stages which are costly in warehouse operations.
So, the transloading in 3pl approach allows businesses to deliver goods to the market more quickly and efficiently.
Read more: Learn How to Ship Freight: Equipment Types, Services, and Sizes
Different types of Transloading in 3pl
Manufacturing transloading:
Manufacturing transloading in 3pl performs when the main distribution center receives products and then arranges them for shipment to different manufacturing locations.
Distributor transloading freight:
In this process, input items are collected from different vendors and then mixed in a product pallet, and it will be sent to the customer after getting the last part.
Transportation transloading:
This service combines different carriers in the less-than-truckload (LTL) and small-package industries to achieve economies of scale.
transloading retail:
In this method, the products are received from several vendors and then categorized on outbound trucks for retail stores.
transloading opportunistic:
Every distribution center can use this. Canada Transloading opportunistic involves the direct transfer of goods from the receiving dock to the shipping area to fulfill an order from the consumer.
Read more: What is delivery management?

Products suitable for transloading in 3PL logistics
Some products are better suited for transloading freight than others. Some of the most common are:
- Items with high quality that do not need inspections during goods receipt
- Perishable items
- Staples retail products with constant demand
- Pre-picked products from another production factory

What Does a Transloader Do?
A transloader is a professional who specializes in the transloading process. Their primary responsibility is to oversee the transfer of goods from one transportation mode to another.
They coordinate the logistics, ensure proper handling of the cargo, and optimize the transloading freight operations for efficiency.
Transloaders are knowledgeable about various transportation modes and understand the specific requirements for each type of cargo. They play a critical role in facilitating smooth and seamless transitions between different modes of transportation, contributing to efficient supply chain management.
Advantages of Transloading in 3PL logistics
- Reduces warehousing charges: Companies need to rent a smaller space to unload their products, so the costs will be much lower than renting a complete warehouse.
- Reduces labor costs: Because of eliminating the need to pick and put away products in the warehouse, Transloading in 3pl will reduce staff costs.
- Reduction of delivery times: Products can reach the customers faster as moving goods from one truck to another is quicker than picking up orders.
- Friendly for the environment: Transloading ensures that fewer trucks or vans with small amounts of products are used, and traveling involves fewer miles.
- Reduction of vehicle costs: As transloading in 3PL logistics companies is usually located near the final destination, less fuel will use in this approach.
- Reduction of damage: During the product handling process, products may inadvertently be damaged by the staff who handle them. As products move less on the transloading (or cross-docking), the possibility of damage is considerably reduced.
Related article: What Is Expedited Shipping & Why Would I Need It
Example of Transloading Service
- Transfer of goods from a truck to a train at a rail terminal. This allows for efficient transportation of cargo over long distances using the rail network.
- Transloading of goods from a container ship to a truck at a port. This enables the cargo to be transported directly to its final destination or to a distribution center for further delivery.
- Transfer of goods from a railcar to a barge, facilitating transportation along inland waterways. This is especially beneficial for bulky or heavy cargo that is more cost-effective to transport by water.
- In the oil and gas industry, transloading services are commonly used to transfer crude oil or refined petroleum products from pipelines to railcars or trucks. This allows for flexible transportation options and ensures the efficient distribution of petroleum products to various markets.
Risks of transloading
- Time-consuming: Transloading is time-consuming as more time to plan and monitor the process is needed.
- Need for reliable suppliers: In transloading, continuous errors will reduce efficiency and increase costs due to late or incorrect deliveries. So, reliable providers are essential to work with cross-docking tasks successfully.
- Transport carriers: A suitable number of carriers and docks are needed for the efficiency of cross-docking, which will increase costs.
Learn more about Courier Service in Canada





